Table of Contents
What is Google Analytics
Google Analytics is like a smart helper for your website. It lets you see how many people visit your site, what they do while they’re there, and where they come from. Here’s what it can do for you:
- See Who’s Visiting: Find out how many visitors you have, which pages they check out, and how long they stay.
- Know Your Audience: Learn about your visitors’ age, gender, where they live, what they’re interested in, and what devices they use.
- Track Their Journey: See how people navigate through your site, which pages they visit first, and what actions they take, like clicking buttons or filling out forms.
- Find Traffic Sources: Discover how people find your site, whether it’s through search engines, social media, direct visits, or links from other websites.
- Measure Success: Set up goals, like purchases or sign-ups, and see how well your site is achieving them.
- Real-Time Updates: Watch in real-time to see who’s on your site right now, what pages they’re viewing, and where they came from.
- Create Custom Reports: Build reports tailored to the specific information you care about the most.
- Track Sales: If you have an online store, monitor your sales, see which products are popular, and understand customer behavior.
- Connect with Other Tools: Integrate with other Google services like Google Ads and Google Search Console to get a full picture of your marketing efforts.
- Monitor Events: Track specific actions on your site, like video plays or downloads, to see how users interact with your content.
Google Analytics is free and incredibly powerful. It gives you the insights you need to make your website better, improve user experience, and fine-tune your marketing strategies. Let get into the nitty gritty now.
What Is Not a Benefit of Google Analytics Remarketing?
Google Analytics Remarketing is a powerful tool that allows businesses to reach potential customers who have previously interacted with their website or app. By leveraging data collected by Google Analytics, businesses can create targeted ads to re-engage these users, potentially leading to higher conversion rates and increased ROI. However, understanding what is not a benefit of Google Analytics remarketing can help in setting realistic expectations and optimizing its use.
1. Immediate Sales Increases
While remarketing can certainly lead to sales, expecting an immediate and substantial increase in sales solely due to remarketing efforts is unrealistic. Remarketing aims to nurture leads and guide them back to your site, but other factors such as the quality of the ad, the appeal of the product, and the overall customer experience play crucial roles in driving sales.
2. Guaranteed User Engagement
Remarketing increases the likelihood of user engagement by reminding potential customers of your brand, but it does not guarantee that users will engage with your ads or website. Factors like ad fatigue, irrelevant ad content, and poorly targeted audiences can all impact engagement rates.
3. Low Advertising Costs
Remarketing campaigns can be cost-effective, but they are not necessarily low-cost. Depending on your industry, competition, and targeting criteria, the cost of remarketing can vary. Additionally, poorly managed campaigns can lead to higher costs without delivering proportional returns.
4. Complete Customer Journey Insights
While Google Analytics provides valuable data on user behavior, it does not offer a complete view of the customer journey. Users may interact with your brand through multiple channels not tracked by Google Analytics, such as offline interactions, other digital platforms, or competitor websites.
5. Universal Applicability
Remarketing is not suitable for all businesses. Certain industries or products might not benefit as much from remarketing due to the nature of their customer base or purchasing behavior. For instance, businesses offering one-time services or highly niche products might not see significant returns from remarketing efforts.
The Five Sections of the Google Analytics Dashboard
Google Analytics is a robust platform that provides detailed insights into website performance and user behavior. The dashboard is divided into five main sections, each offering a different perspective on the data collected.
1. Real-Time Overview
The Real-Time section provides live data about the current activity on your website. You can see the number of active users, their geographic locations, the pages they are viewing, and other immediate interactions. This section is useful for monitoring the immediate impact of marketing campaigns or website changes.
2. Audience Overview
The Audience section gives insights into the characteristics of your website visitors. This includes demographics, interests, geographic locations, and technology used to access your site. Understanding your audience helps tailor content and marketing strategies to better meet their needs.
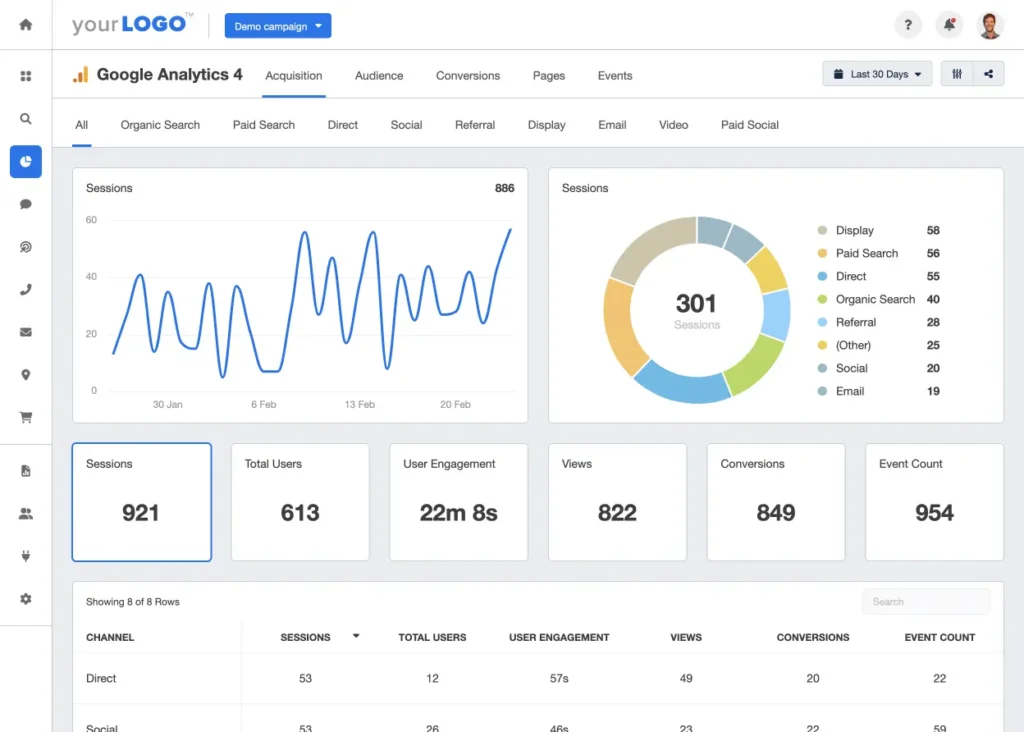
3. Acquisition Overview
The Acquisition section focuses on how users arrive at your website. It breaks down traffic sources such as organic search, paid search, social media, referrals, and direct visits. Analyzing this data helps optimize marketing efforts and understand which channels are most effective.
4. Behavior Overview
The Behavior section tracks user interactions on your website, such as page views, bounce rate, and average session duration. It also includes data on specific events, such as clicks on buttons or downloads. This information helps identify areas for improving user experience and content effectiveness.
5. Conversion Overview
The Conversion section measures how well your website meets its business goals. This includes tracking specific actions users take, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter. Setting up goals and e-commerce tracking in this section is crucial for measuring the success of your website and marketing efforts.
Understanding Each Section of the Google Analytics Dashboard
Each section of the Google Analytics dashboard provides a unique view of your website data. Here’s a deeper look into what you can find in each section:
Audience Overview
- Demographics: Age and gender distribution of your visitors.
- Interests: Categories and topics your visitors are interested in.
- Geo: Geographic locations and languages spoken by your visitors.
- Behavior: New vs. returning visitors, frequency, and engagement metrics.
- Technology: Browsers, operating systems, and devices used by your visitors.
Acquisition Overview
- Channels: Breakdown of traffic sources such as organic, paid, social, referral, and direct.
- Campaigns: Performance data for specific marketing campaigns.
- Source/Medium: Detailed insights into where your traffic is coming from.
- Search Console: Integration with Google Search Console for organic search performance data.
Behavior Overview
- Site Content: Page views, unique page views, average time on page, and bounce rate.
- Site Speed: Page load times and other performance metrics.
- Site Search: Usage of your website’s internal search function.
- Events: Tracking of specific user interactions like clicks, downloads, and video plays.
- Behavior Flow: Visualization of user journeys through your website.
Conversion Overview
- Goals: Tracking of specific actions such as form submissions, sign-ups, and purchases.
- E-commerce: Detailed insights into sales performance, including product performance and transactions.
- Multi-Channel Funnels: Analysis of how different marketing channels contribute to conversions.
- Attribution: Models that attribute credit to different touchpoints in the customer journey.
Types of Hits Tracked by Google Analytics
Google Analytics tracks various types of hits, which are interactions that send data to the platform. Understanding these hits is essential for accurate data analysis.
Pageview Hits
A pageview hit is recorded each time a user loads a page on your website. This is the most common type of hit and provides data on which pages are being viewed and how often.
Event Hits
Event hits track specific interactions on your website that do not involve loading a new page, such as clicks on buttons, downloads, and video plays. Event tracking requires additional setup but offers valuable insights into user behavior.
Transaction Hits
Transaction hits, also known as e-commerce hits, track purchase data on your website. This includes transaction details, product information, and revenue generated. Setting up e-commerce tracking is crucial for online stores to measure sales performance.
Social Hits
Social hits track interactions with social sharing buttons on your website. This data helps measure the impact of social media integration and sharing activity on your site.
What Does Event Count Mean in Google Analytics?
The event count in Google Analytics refers to the total number of times a specific event is triggered on your website. Events are user interactions that you define and track, such as button clicks, video plays, or form submissions.
Importance of Event Tracking
Event tracking is crucial for understanding how users interact with your website beyond simple page views. It provides insights into user engagement and helps identify which elements of your site are most effective in driving desired actions.
How to Set Up Event Tracking in Google Analytics
- Define Events: Determine the specific interactions you want to track.
- Add Tracking Code: Implement the appropriate tracking code on your website. This typically involves using Google Tag Manager for easier management.
- Configure Tags: Set up tags in Google Tag Manager to track the defined events.
- Verify Data: Check your Google Analytics account to ensure that event data is being collected correctly.
Analyzing Event Data in Google Analytics
Once event tracking is set up, you can analyze the data in the Behavior section of Google Analytics. This includes:
- Event Category: The broadest level of classification, such as “Videos” or “Downloads”.
- Event Action: The specific action taken, like “Play” or “Click”.
- Event Label: Additional information about the event, such as the name of the video or file downloaded.
- Event Value: A numeric value associated with the event, which can be used for further analysis.
Best Practices for Using Google Analytics
- Set Clear Goals: Define what you want to achieve with your website and track relevant metrics.
- Regularly Review Data: Monitor your Google Analytics data frequently to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Use Segments: Create custom segments to analyze specific subsets of your data, such as new vs. returning visitors.
- Integrate with Other Tools: Enhance your analysis by integrating Google Analytics with other tools like Google Ads and Google Search Console.
- Continuously Optimize: Use the insights gained from Google Analytics to make data-driven decisions and continuously optimize your website and marketing strategies.
Conclusion
Google Analytics is a powerful tool that provides comprehensive insights into your website’s performance and user behavior. Understanding the benefits and limitations of remarketing, the structure of the Google Analytics dashboard, the types of hits tracked, and the significance of event counts can help you make informed decisions and optimize your online presence.
Read this article to learn how to check competitor’s website traffic.
FAQs
What is not a benefit of Google Analytics remarketing?
Google Analytics remarketing does not guarantee immediate sales increases, guaranteed user engagement, low advertising costs, complete customer journey insights, or universal applicability.
What are the five sections of the Google Analytics dashboard?
The five sections are Real-Time Overview, Audience Overview, Acquisition Overview, Behavior Overview, and Conversion Overview.
Which kinds of hits does Google Analytics track?
Google Analytics tracks pageview hits, event hits, transaction hits, and social hits.
What does event count mean in Google Analytics?
Event count refers to the total number of times a specific event is triggered on your website.
How can I set up event tracking in Google Analytics?
Define the events, add the tracking code, configure tags in Google Tag Manager, and verify the data in Google Analytics.
Why is event tracking important for my website?
Event tracking is important because it provides insights into user interactions beyond page views, helping to understand user engagement and the effectiveness of website elements.
Leave a Reply